Our Commitment to a Greener Future


In the world of electronics, the efficiency and effectiveness of PCB assembly prototyping stand as a critical determinant of success. Industry expert Dr. Emily Thompson, a leading figure in electronic design and prototyping, emphasizes the importance of this phase, stating, "A well-executed PCB assembly prototype can significantly reduce time to market and enhance product reliability." This highlights that understanding the intricacies of PCB assembly prototyping is essential for engineers and designers looking to bring their innovative ideas to life.
As the demand for faster and more efficient prototyping processes continues to grow, mastering the essential tips for successful PCB assembly is paramount. From choosing the right materials to optimizing the design for manufacturability, each step directly impacts the final product's performance. Whether you are a seasoned professional or just entering the field, grasping the nuances of PCB assembly prototypes will empower you to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to improved outcomes in the design and manufacturing process. By incorporating best practices and learning from industry leaders, you can enhance your proficiency in this vital aspect of electronics development.

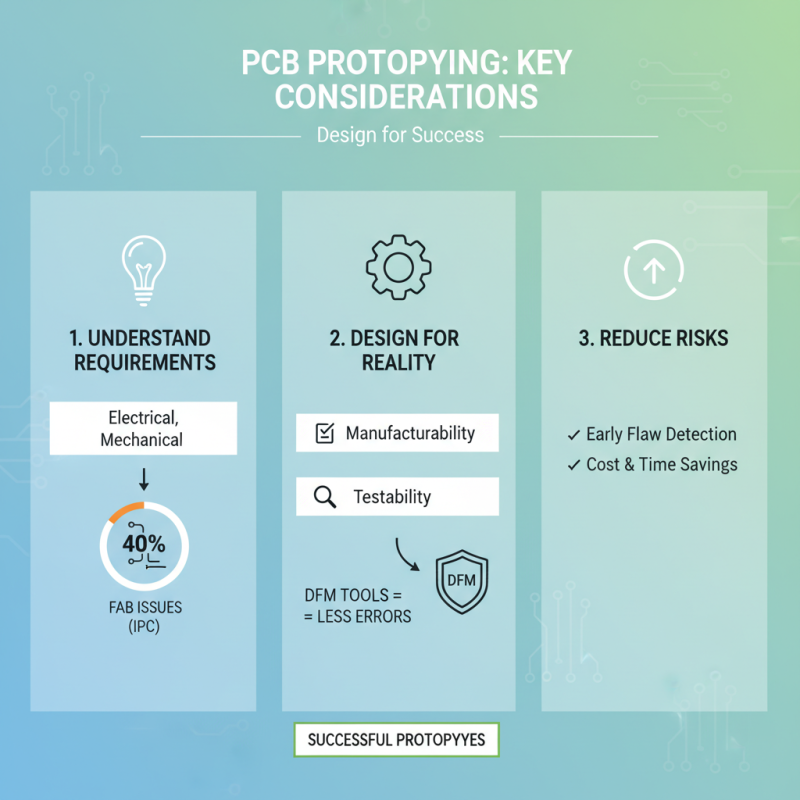
When it comes to PCB design in prototyping, several essential considerations can significantly influence the success of the project. Firstly, understanding the requirements for the prototype is crucial. According to a report by the IPC (Institute of Printed Circuits), nearly 40% of PCB fabrication issues stem from inadequate design preparation. Effective design needs not only to account for electrical functionality but also aspects like manufacturability and testability. Employing tools like Design for Manufacturability (DFM) can help identify potential flaws early, reducing costly errors and delays later on in the assembly process.
Additionally, the choice of materials and components plays a vital role in prototyping success. According to a study by Grand View Research, demand for advanced PCBs is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 5% through 2025, highlighting the importance of selecting high-quality materials that can endure performance requirements and environmental conditions. Designers should evaluate the thermal management capabilities of components as overheating is one of the leading causes of failure in prototypes. Investing time in researching and selecting appropriate materials not only enhances the longevity of the PCB but also aligns with industry trends towards more sustainable and efficient electronics manufacturing.
When engaging in PCB assembly prototyping, selecting the right materials and components is crucial for ensuring efficiency and effectiveness. Key materials include high-quality substrates like FR-4, which is popular for its excellent electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength. A good substrate not only supports the circuit traces but also maintains the integrity of the components mounted on it. Copper is the standard choice for conductive traces due to its high conductivity and reliability. Ensuring that you have the right thickness and finish can make a significant difference in performance.
In addition to substrates and copper, the choice of components greatly impacts the overall success of the PCB prototype. Utilizing reliable passives like resistors and capacitors that can handle the desired specifications is essential. For active components, consider factors such as power ratings and thermal performance, as these will directly affect the circuit's functionality and lifespan. Moreover, implementing proper soldering techniques with the right solder materials—such as lead-free solder—will enhance the durability of the connections, minimizing issues such as cold solder joints or thermal fatigue. Choosing the right combination of these materials and components not only streamlines the assembly process but also optimizes the performance of the final product.
Testing and validation are paramount in the PCB prototyping process, serving as the cornerstone for ensuring functionality and reliability in the final product. Before a prototype can advance to full-scale production, it is essential to conduct comprehensive testing that covers various operational scenarios.
This includes functional testing, in which the prototype is subjected to its intended operational parameters to confirm that all components interact correctly. Additionally, environmental testing can expose the prototype to conditions such as extreme temperatures or humidity, helping to identify potential issues that could arise in real-world applications.
The validation process goes hand-in-hand with testing, serving to verify that the design meets the initial specifications and performance criteria. Utilizing techniques such as design reviews and benchmark comparisons against established standards can illuminate any discrepancies. Moreover, incorporating feedback from the testing phase into iterative design cycles can lead to enhancements and refinements. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also contributes to a more user-friendly and dependable final product, paving the way for successful implementation in the market.
When sourcing PCB prototyping services, it’s crucial to consider several best practices that can significantly impact the success of your project. First, evaluate the experience and reputation of potential suppliers. Look for companies that have a proven track record in the industry and can provide references or case studies showcasing their capabilities. A reputable service provider is more likely to deliver quality results aligned with your specifications.
Another essential tip is to establish clear communication from the outset. Discuss your project requirements in detail, including your design files, timelines, and budget constraints. This clarity helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that the manufacturer can meet your expectations. Additionally, consider starting with a smaller prototype run to test the service provider’s quality and responsiveness before committing to larger orders.
Finally, pay close attention to the quoting process. A detailed quote should break down the costs associated with materials, assembly, and any additional services. Ensure that the quote includes timelines for delivery and any potential pitfalls that might delay the project. By prioritizing these best practices, you can streamline the PCB prototyping process and set a solid foundation for successful product development.
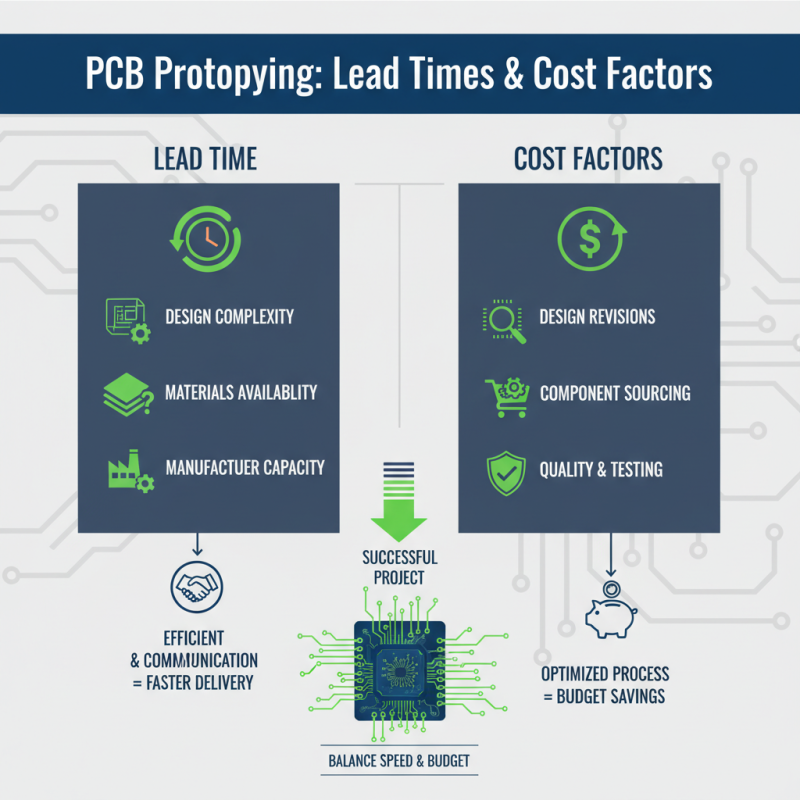
When it comes to PCB prototyping, understanding lead times and cost factors is essential for a successful project. Lead time refers to the duration required to design, manufacture, and assemble a printed circuit board before it can be tested and deployed. This timeline can vary greatly depending on several factors, including the complexity of the PCB design, the availability of materials, and the capacity of the chosen manufacturer. Efficient planning and communication with the production team can help minimize these lead times, ensuring that the design process aligns with development schedules.
Cost is another critical element in PCB prototyping that can significantly impact the overall project budget. There are several cost factors to consider, including material costs, labor, and equipment usage. Choosing the right components and optimizing the design for manufacturability can help keep costs down. In addition, bulk purchasing of materials can reduce expenses, as suppliers often offer discounts on larger orders. Balancing these elements while maintaining quality is key to successful PCB prototyping, allowing engineers and designers to innovate without exceeding budget constraints. Understanding these lead times and cost factors will empower teams to make informed decisions throughout the prototyping process.