Our Commitment to a Greener Future


In today's fast-paced manufacturing environment, electronic board assembly (EBA) has become a cornerstone of efficiency. Experts emphasize its critical role. Dr. Emily Chen, a leading authority in electronic manufacturing, stated, “Without effective electronic board assembly, innovation slows down significantly.” This sentiment resonates across industries that rely on complex electronic systems.
Electronic board assembly is integral to producing high-quality electronic devices. It connects components and conducts energy flow to ensure optimal performance. Each assembly process must be precise and error-free, which poses challenges to manufacturers. A small mistake can disrupt an entire production line, leading to delays and additional costs.
As technology advances, the demand for sophisticated electronic board assembly increases. Companies must adapt to these changes or risk falling behind. The pressure to innovate is immense. In this context, while the importance of effective EBA is clear, the complexity cannot be overlooked. Many organizations find themselves grappling with outdated techniques. Transforming these processes is essential for thriving in modern manufacturing.

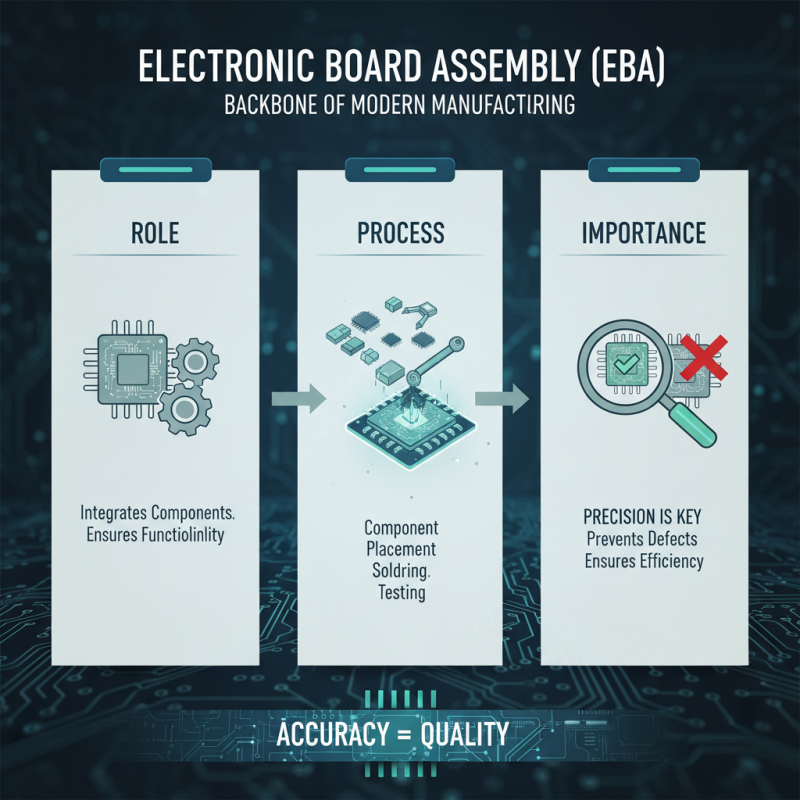
In modern manufacturing, Electronic Board Assembly (EBA) plays a pivotal role. It is the backbone of many electronic products. EBA integrates various components onto a circuit board. This process ensures functionality and efficiency in production. Precision is key here. A small error can lead to significant issues. Manufacturers must focus on accuracy during assembly.
Tips: Regularly train staff on assembly techniques. Small, consistent training can reduce errors. Assess your equipment often. Outdated tools can hinder the assembly process.
EBA also faces challenges. The complexity of designs increases with technology. Manufacturers must adapt to these changes quickly. Supply chain disruptions can impact the availability of components. It’s crucial to establish strong supplier relationships. Not all manufacturing facilities can handle sophisticated boards. Some may struggle with high-volume production.
Tips: Consider investing in modular equipment. This allows for flexible assembly lines. Encourage feedback from your assembly team. They often have insights that can improve processes.
Electronic Board Assembly (EBA) is crucial for today's manufacturing landscape. It integrates multiple technologies, enhancing efficiency and precision. One key technology in this realm is Surface Mount Technology (SMT). SMT allows components to be mounted directly onto the surface of circuit boards. This method reduces space and increases the density of components. However, achieving the ideal placement can be challenging. Misalignment can lead to malfunctioning devices.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) plays a vital role in ensuring quality. It uses cameras to check the assembly for defects. AOI can detect soldering errors and misplaced components. While highly effective, it is not infallible. False positives can occur, leading to unnecessary rework. Another important technology is Pick and Place machines. These machines automate the placement of components, speeding up production. Yet, programming these machines requires a skilled operator. Inaccurate programming can result in significant setbacks.
The integration of these technologies creates a dynamic assembly process. Each step offers opportunities for improvement. Embracing innovation is essential. However, manufacturers must also address the challenges that arise. Balancing speed, accuracy, and cost remains a constant struggle in EBA. Continuous evaluation of technologies can help refine the process.
This chart illustrates the adoption rates of key technologies in electronic board assembly (EBA) across various sectors in modern manufacturing.
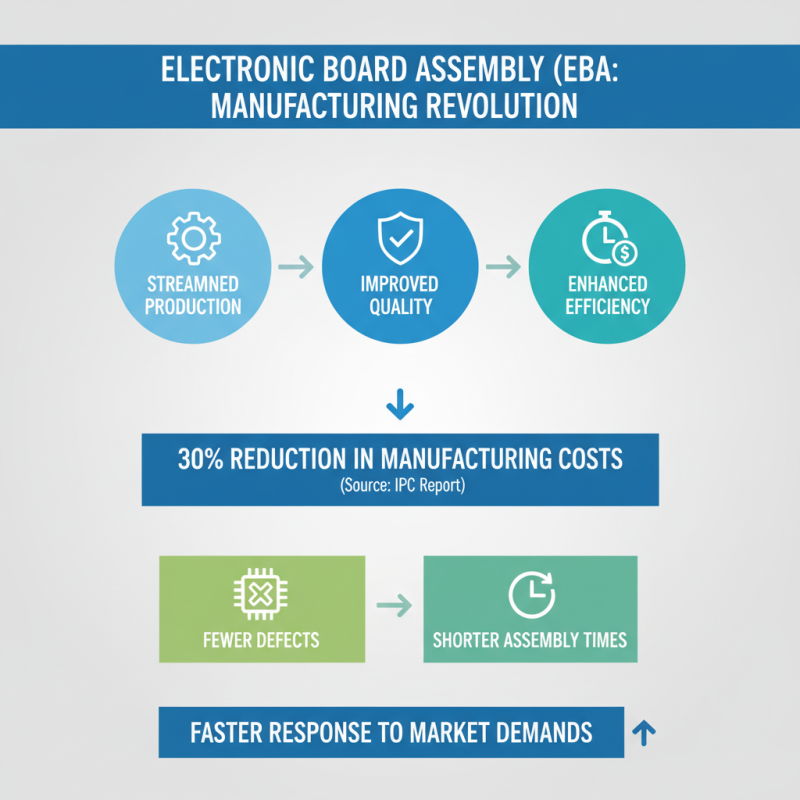
Electronic Board Assembly (EBA) is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. It streamlines production lines, improves product quality, and enhances efficiency. According to a report by IPC, companies that adopt EBA can see a 30% reduction in manufacturing costs. This reduction comes from fewer defects and shorter assembly times. With this approach, manufacturers can respond faster to market demands.
Quality is a key benefit of EBA. The use of automated assembly machines ensures precision. A study by Deloitte revealed that automation can increase production quality by 40%. This leads to fewer recalls and higher customer satisfaction. However, not all manufacturers have fully embraced this technology. Some still rely on outdated methods. This reliance can hinder their competitiveness in a rapidly changing market.
Efficiency is another crucial aspect of EBA. Data from a McKinsey report shows that companies utilizing EBA improve their turnaround times by up to 50%. Many firms struggle to keep pace with demand. In contrast, those using electronic assemblies can scale their operations effectively. This disparity highlights a critical need for industries to adapt. Without embracing EBA, manufacturers risk falling behind competitors who leverage technology for better performance.
In the realm of electronic board assembly (EBA), manufacturers face several challenges. A recent industry report indicates that defects in the assembly process can lead to a staggering 15% loss in production efficiency. This is primarily due to issues like insufficient training and outdated technology. Many companies struggle to adapt to rapid technological changes, which can hinder their competitiveness.
Another challenge is the integration of automated systems. While automation has great potential, nearly 30% of manufacturers report difficulties in implementation. Workers often resist change, fearing job loss or difficulty in adapting. If managers do not address these concerns, it can lead to reduced morale and productivity.
Quality control remains a critical area for improvement. Studies show that up to 20% of assembled boards fail quality tests. Implementing real-time monitoring and adaptive feedback systems can help reduce this statistic. However, many companies still rely on outdated inspection methods. Addressing these challenges requires both investment in technology and a commitment to workforce development.
As electronic board assembly continues to evolve, its impact on modern manufacturing becomes more pronounced. Advanced technologies like automation and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing this field. These innovations enhance production speed and accuracy, but they come with challenges. Adapting to these fast-paced changes can be overwhelming for many manufacturers.
Moreover, industry experts predict a growing focus on sustainability. Eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient processes are becoming essential. Balancing efficiency with environmental responsibility is no small feat. Some companies struggle to incorporate green practices, often prioritizing cost over sustainability. This creates a tension between innovation and ethical manufacturing.
Furthermore, the rise of smart factories is reshaping the landscape. Integrating IoT devices enables real-time data analysis, which can improve assembly processes. However, the reliance on technology raises concerns about cybersecurity. Manufacturers will need to rethink their approach to security. As these trends unfold, a continuous commitment to improvement and adaptability is crucial for success in the electronic board assembly sector.