Our Commitment to a Greener Future


Designing a circuit board can appear daunting for beginners, yet it is an essential skill in the electronics industry, which has seen significant growth in recent years. According to a report from the Electronics Industry Association (EIA), the global printed circuit board market is projected to reach $90 billion by 2025, driven by expanding consumer electronics and IoT applications. As such, understanding the fundamentals of circuit board design is paramount for emerging engineers and hobbyists looking to enter this thriving field.
Renowned circuit design expert Dr. Emily Wang states, “A well-designed circuit board is not just a piece of hardware; it’s the foundation of innovation in electronics.” This highlights the importance of adopting best practices and a systematic approach to designing circuit boards. By learning the underlying principles and applying industry standards, beginners can avoid common pitfalls and enhance their design efficiency. This introduction to circuit board design will provide insights into essential tips and practical strategies to help novices navigate through their initial projects, paving the way for more advanced applications and contributing to the ever-growing electronics ecosystem.

Understanding the basics of circuit board design is an essential first step for beginners eager to dive into electronics. At its core, a circuit board serves as the framework for connecting electronic components. Familiarizing oneself with fundamental concepts such as the different types of circuit boards, commonly used materials, and design principles is crucial. Typically, a printed circuit board (PCB) is made from insulating substrates that prevent unwanted electrical connections and ensure the components function as intended.
Once the foundational knowledge is established, understanding the layout process becomes critical. Beginners should learn how to create a schematic diagram that represents the circuit’s flow, specifying where each component will be placed. After that, transitioning to PCB layout involves arranging the components on the board and routing electrical connections between them. It's important to pay attention to spacing and signal integrity to avoid issues such as interference. By following best practices like creating a well-organized design and keeping trace lengths short, novice designers can minimize problems and lead to more efficient and reliable final products.
| Step | Description | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define circuit requirements | Understand voltage, current, and component specifications. |
| 2 | Create a schematic diagram | Use software like Eagle or KiCAD for accuracy. |
| 3 | Design the PCB layout | Keep traces short and minimize bends in routing. |
| 4 | Select materials | Consider thermal and electrical properties. |
| 5 | Test the prototype | Validate performance and check for errors. |
| 6 | Finalize design | Incorporate feedback and prepare for production. |
When embarking on the journey of designing circuit boards, having the right tools and software is crucial to streamline the process and achieve professional-quality results. Essential tools typically include a reliable soldering iron, multimeter, and oscilloscope, which are fundamental for testing and troubleshooting circuits. However, the backbone of modern circuit board design lies in software applications that enable engineers to create accurate schematics and layouts efficiently. According to a recent market report, the global electronic design automation (EDA) software market was valued at approximately $11 billion in 2022, and it is projected to witness substantial growth as more individuals and organizations leverage these innovative tools in their design processes.
Software options range from beginner-friendly applications to advanced platforms used by seasoned engineers, offering functionalities like real-time simulation and collaborative features. For instance, many design tools now integrate algorithms that optimize layouts, dramatically reducing time spent on revisions and enhancing overall performance. Industry reports indicate that utilizing these sophisticated software solutions can decrease the design cycle by up to 60%, allowing innovators to bring their products to market faster. Emphasizing the importance of choosing appropriate software that aligns with individual skill levels will significantly impact the success of circuit board design projects.
This bar chart illustrates the popularity of various circuit board design tools among beginners. The data indicates that Altium and Eagle are the most favored tools for circuit board design, while Fritzing and KiCAD take a slightly lesser preference. Understanding these trends can help beginners make informed decisions on which software to explore.
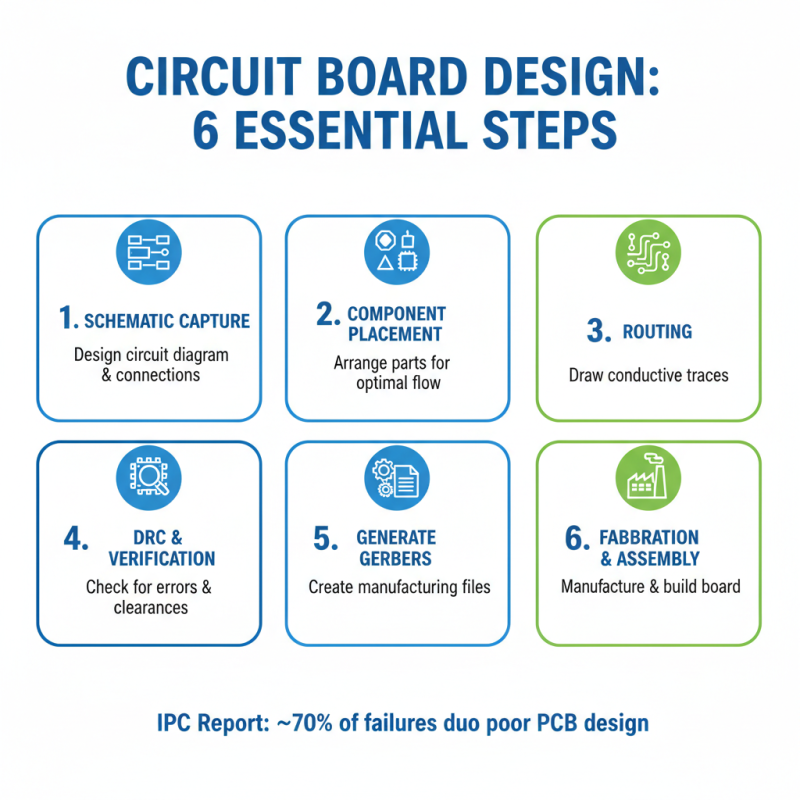
Creating a circuit board layout involves several key steps that can guide beginners in designing effective and efficient boards. First, it’s essential to understand the basic concepts of circuit design, including the function of each component and how they interconnect. A recent report from the IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) indicates that nearly 70% of electronic failures are attributed to poor PCB design. Thus, following a structured process can help mitigate these risks.
The step-by-step process begins with schematic capture, where the circuit is visually represented. Next, choose a PCB design software that suits your needs; many user-friendly options cater to beginners. As you translate the schematic into a PCB layout, consider factors like trace width, spacing, and component placement to ensure optimal performance and manufacturability. A guideline by The Electronics Components Industry indicates that a well-designed board can reduce manufacturability issues by up to 30%, emphasizing the importance of proper layout. Finally, run a design rule check (DRC) to catch any potential errors before moving onto prototyping and testing your circuit board. This meticulous planning and execution set the foundation for a successful circuit board design.
When designing a circuit board, beginners often fall into several common traps that can hinder the performance and functionality of their projects. One significant mistake is neglecting to plan the layout carefully. A poorly organized design can lead to signal integrity issues, such as crosstalk and interference. It’s crucial to think through the placement of components and the routing of traces before diving into the design software.
Utilizing proper spacing and understanding how electrical signals travel can greatly reduce potential problems down the line.
Another frequent error is failing to consider the power requirements adequately. Beginners may overlook the importance of providing sufficient power to each component, resulting in instability or malfunction. It’s vital to not only calculate the total current requirement but also to examine the voltage levels needed for each part of the circuit.
Overloading traces can lead to overheating and damage, so designing with appropriate width and thickness according to current levels can prevent these issues. In addition, ignoring thermal management can lead to performance degradation; thus, incorporating methods for heat dissipation is essential in the design process.
When designing a circuit board, testing and prototyping are critical stages that cannot be overlooked. According to a 2022 study by the Electronics Industry Association, nearly 30% of projects fail to meet their initial performance expectations due to inadequate testing processes. Therefore, implementing robust testing methods during the prototyping phase is essential for ensuring reliability and functionality.
One effective approach is to utilize simulation software that allows designers to predict how their circuit will behave under various conditions. This not only saves time but also minimizes costly mistakes during the fabrication phase. Additionally, incorporating automated testing tools can enhance the efficiency of the testing process, providing quick feedback on circuit performance. Remember, the earlier issues are identified, the less likely they are to result in significant project setbacks.
Tip: Always create multiple prototypes of your circuit design. This practice allows for comprehensive testing across different scenarios, leading to refined designs that maximize performance and minimize errors. Furthermore, consider peer reviews of your prototypes to gain insights from fellow designers who may catch overlooked discrepancies or suggest improvements. A collaborative approach can significantly enhance the overall quality of your circuit board design.